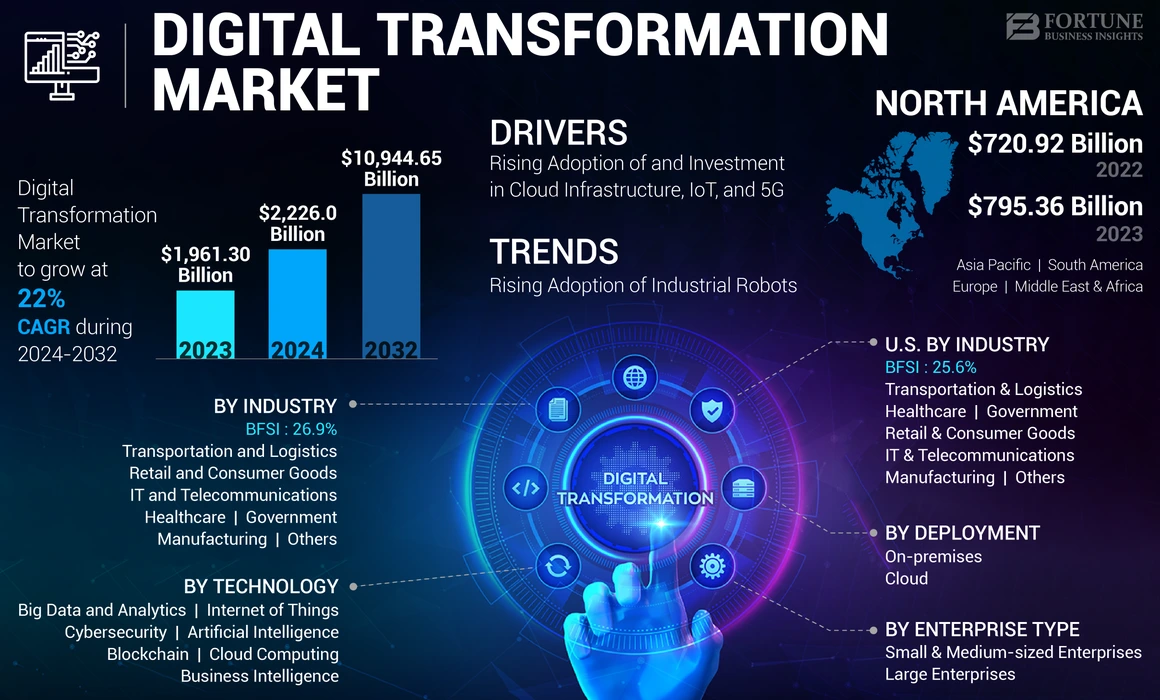
In the wave of Industry 4.0 and digital transformation, equipment maintenance has long moved past the passive mode of “repairing after failure.” According to the “Digital Transformation Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis” report by Fortune Business Insights, the global digital transformation market size reached $1.96 trillion in 2023 and is projected to exceed $10.9 trillion by 2032, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 22%. As the core link connecting technology with asset value, Enterprise Smart Maintenance is becoming a key driver for cost reduction and efficiency improvement in industries such as manufacturing, energy, and cultural tourism.
particularly in the manufacturing sector, the installation of industrial robots reached 553,000 units in 2022 and is expected to break 600,000 units in 2024. The increase in equipment automation directly drives the demand for Enterprise Smart Maintenance in manufacturing enterprises—traditional manual maintenance can no longer match high-density, highly interconnected intelligent equipment. AI-driven Enterprise Smart Maintenance has become the core path to solving this challenge. For enterprises, understanding the essence of Enterprise Smart Maintenance while implementing adaptable solutions is no longer just a “bonus item,” but a “mandatory course” to ensure production continuity and enhance core competitiveness.
I. Enterprise Smart Maintenance: A New Paradigm of Data-Driven Maintenance
In traditional maintenance models, the limitations of “periodic maintenance” and “post-event repair” are becoming increasingly prominent—excessive maintenance causes waste of manpower and spare parts, while sudden failures can lead to production line stoppages, where a single hour of downtime on a production line can result in losses of tens of thousands of dollars. The emergence of Enterprise Smart Maintenance has completely reconstructed this logic. It is not simply a “stacking of technologies,” but a fundamental shift from “passive response” to “active prediction,” centered on data and integrating technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Big Data analytics.
From a definition standpoint, Enterprise Smart Maintenance is a closed-loop system of “Sense-Analyze-Decide-Execute”: IoT sensors collect real-time equipment operation data such as vibration, temperature, and energy consumption; AI algorithm models deeply analyze equipment health status to identify potential failure risks in advance; maintenance work orders are automatically triggered, and spare parts resources are scheduled; finally, maintenance personnel execute tasks efficiently via mobile terminals. Compared to traditional models, the greatest advantage of this AI-driven Enterprise Smart Maintenance lies in “precision”—precise identification of fault nodes, precise planning of maintenance times, and precise matching of resource needs, upgrading maintenance work from being “experience-driven” to “data-driven.”
II. The Core Value of Enterprise Smart Maintenance: Addressing Industry Operations Pain Points directly
1. Manufacturing-Specific Value: Solving the Equipment Linkage Challenge
For manufacturing companies, the value of manufacturing Enterprise Smart Maintenance is particularly outstanding. Manufacturing equipment is dense, and production line linkage is strong; a minor fault in one machine can trigger a chain reaction. Data from an automotive parts manufacturer shows that after introducing Enterprise Smart Maintenance, the unplanned downtime rate dropped by 28%, and maintenance costs decreased by 22%. This is a direct embodiment of the core value of smart maintenance. Specifically, the core value of Enterprise Smart Maintenance can be broken down into four dimensions, each directly addressing corporate operational pain points.
2. Reducing Unplanned Downtime Risks and Ensuring Production Continuity
Unplanned downtime is the “invisible killer” of manufacturing. According to statistics from industrial equipment associations, under traditional maintenance models, downtime caused by sudden equipment failures accounts for 45% of total maintenance time. However, Enterprise Smart Maintenance uses AI algorithms for real-time monitoring and trend analysis of equipment data, enabling the prediction of potential failures 3-7 days in advance. For example, by monitoring abnormal fluctuations in motor vibration frequency, bearing wear can be predicted, allowing maintenance personnel to complete repairs before a failure occurs. This “predictive maintenance” mode transforms equipment downtime from “sudden and uncontrollable” to “planned and controllable,” maximizing the reduction of production interruption losses.
3. Optimizing Maintenance Cost Structure and Achieving Efficient Resource Allocation
In traditional maintenance, “over-maintenance” and “spare parts backlog” are common issues. An energy company once spent an extra 1.2 million yuan annually on maintenance fees due to replacing equipment filters on a fixed cycle; meanwhile, unreasonable spare parts inventory reserves tied up over 8 million yuan in working capital. Enterprise Smart Maintenance accurately determines maintenance needs through data, avoiding “meaningless maintenance”; simultaneously, it precisely allocates spare parts based on failure predictions, reducing inventory backlog. Paired with a comprehensive Enterprise Smart Maintenance solution, companies can achieve the optimal match of maintenance manpower and spare parts resources. Estimates show that this can reduce comprehensive maintenance costs by an average of 15%-30%.
4. Extending Equipment Lifespan and Enhancing Asset ROI
Production equipment is a core asset for enterprises, and its lifespan directly affects the Return on Investment (ROI). In traditional maintenance, due to the untimely discovery of faults, the wear and tear of certain equipment components can accelerate the aging of the entire machine. Enterprise Smart Maintenance, through full-lifecycle data monitoring, can not only handle minor faults in time but also optimize operating standards based on equipment running data—for example, analyzing the pressure parameters of an injection molding machine to adjust production processes and reduce equipment wear. Data shows that equipment applying AI-driven Enterprise Smart Maintenance has an average lifespan extension of 15%-20%, allowing the enterprise’s asset value to be maximized.
5. Supporting Compliance Management and Assisting Sustainable Development
In strictly regulated industries such as energy and healthcare, the integrity and standardization of equipment maintenance records are core requirements for compliance inspections. Enterprise Smart Maintenance systems can automatically record equipment operation data, maintenance processes, and spare parts replacement information, forming immutable electronic archives to easily cope with compliance audits. At the same time, precise maintenance planning reduces energy waste and spare parts consumption, helping enterprises achieve “Double Carbon” goals. After a chemical enterprise introduced manufacturing Enterprise Smart Maintenance, equipment energy consumption dropped by 12%, and carbon emissions were indirectly reduced by 9%, achieving a win-win for economic and social benefits.

III. SME Transformation Path: Lightweight Solutions to Break Barriers
It is worth noting that Enterprise Smart Maintenance is not the “exclusive product” of large enterprises. With the development of SaaS technology, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can also achieve precise transformation through tiered product solutions, among which 313FM Cloud Inspection and SAMEX EAM are highly representative choices.
313FM Cloud Inspection: As a lightweight solution focusing on patrol and inspection, it perfectly fits the “small investment, quick implementation” needs of SMEs. It requires no complex deployment and allows for the rapid establishment of equipment inspection processes, supporting inspection task distribution, real-time data uploading, and one-click anomaly reporting. It is particularly suitable for small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises or property management units with a moderate number of equipment and core needs focused on on-site inspection.
SAMEX EAM: If an enterprise requires more comprehensive asset full-lifecycle management capabilities, SAMEX EAM provides an integrated solution covering equipment ledgers, maintenance management, spare parts inventory, and cost accounting. Its flexible module combination mode allows SMEs to enable core functions first and gradually expand later, avoiding resource waste. For example, a small to medium-sized machining factory initially solved low inspection efficiency issues through 313FM Cloud Inspection. As the business developed, they introduced the maintenance management module of SAMEX EAM. Using only 30% of traditional maintenance costs, they achieved a dual effect of a 20% reduction in equipment downtime rate and an 18% reduction in spare parts inventory costs.
IV. Future Trends: AI and Digital Twins Open New Dimensions
In the future, with the integration of AI large models and Digital Twin technology, Enterprise Smart Maintenance will achieve breakthroughs in higher dimensions—simulating equipment operation scenarios through digital twins to deduce the impact of failures in advance; and utilizing large models to achieve automatic accumulation of maintenance knowledge and intelligent Q&A. For enterprises, deploying Enterprise Smart Maintenance now is not only about solving current maintenance pain points but also about reserving core capabilities for future digital competition. Choosing an Enterprise Smart Maintenance solution adapted to one’s own industry scenario allows data to truly become the “baton” of equipment maintenance, enabling the maintenance of stable production advantages and cost advantages in fierce market competition.








