Background of the Incident: The Beginning of Equipment Management Failures
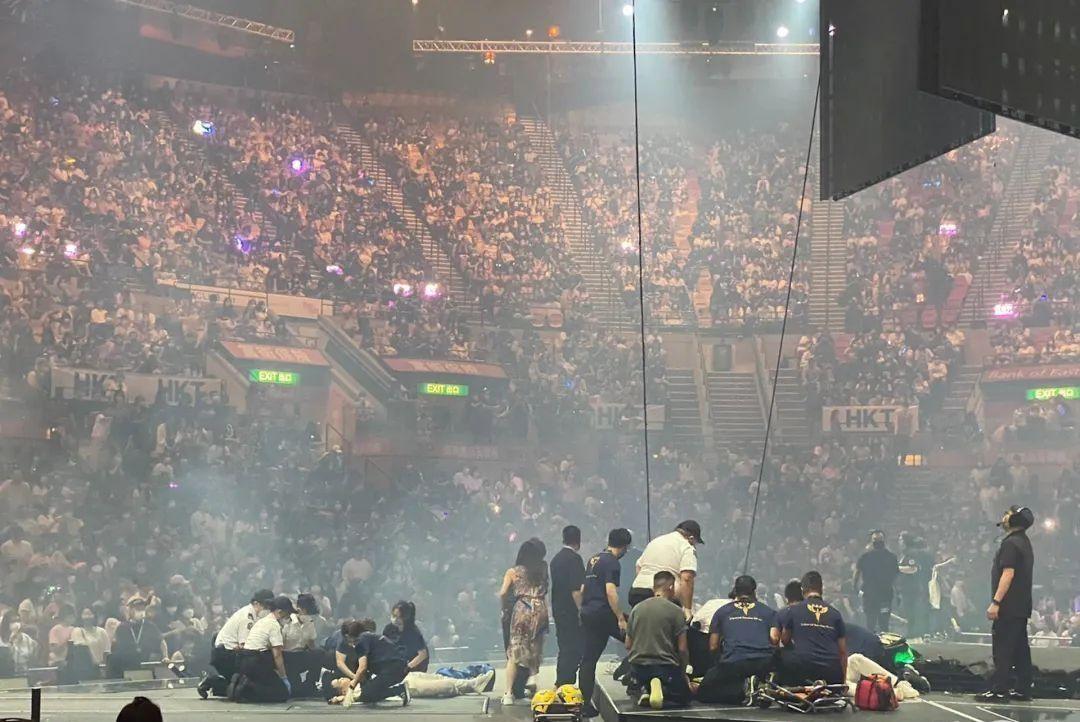
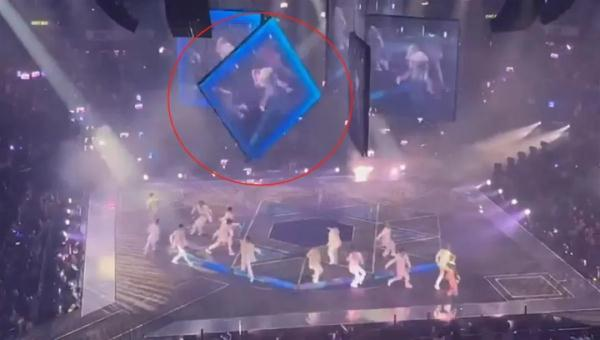
On July 28, 2022, a shocking safety incident occurred at Hong Kong’s Hung Hom Coliseum. During a MIRROR concert held that evening, a massive LED screen suddenly fell from above the stage, directly striking two dancers who were performing at the time. This heart-wrenching accident not only left the audience in shock but also sparked widespread concern and discussion across Hong Kong society.
At the time of the incident, the Coliseum was packed with thousands of excited fans eager to enjoy the performance of their idols. However, the moment the screen fell, the atmosphere in the venue turned into one of horror. Screams and chaos quickly spread throughout the arena. Many members of the audience witnessed the entire tragedy unfold, particularly the moment when one of the dancers (Lee Kai-Yin, stage name Mo) suffered severe spinal injuries, resulting in partial paralysis. This tragedy left an indelible psychological scar on countless individuals. Videos of the incident circulated on social media in the aftermath, further amplifying public awareness of the severity of the event and the hidden dangers of stage safety. ( View Original Report )
This avoidable accident not only caused immense harm to the victims and their families but also raised serious concerns about the safety management of large-scale performance events. As one of Hong Kong’s most iconic performance venues, the Coliseum’s safety failure exposed significant shortcomings in equipment management and safety supervision.
Investigation Results: Management Negligence and Regulatory Failures
Following the incident, the Hong Kong Police quickly launched an investigation, with the case being handled by the West Kowloon Regional Crime Unit. After a thorough inquiry, the police revealed the primary causes of the accident, uncovering multiple areas of mismanagement:
Negligence by the Main Contractor and Stage Engineering Company
The main contractor and the stage engineering company responsible for the concert failed to implement measures to ensure that the stage equipment met necessary safety standards.
The main contractor, in an attempt to expedite the approval process, allegedly falsified the actual weight of the LED screen, leading to an inaccurate assessment of its load-bearing capacity during installation.
Early Signs of Equipment Problems
On the morning of the accident, the LED screen in question had already exhibited abnormalities during its lifting operation. However, staff from the stage engineering company merely performed a simple adjustment and failed to report the issue to anyone or undertake further repairs or corrective measures.
Lack of Professional Inspection
After the lifting device was installed, no qualified engineers were assigned to conduct a detailed inspection. As a result, the equipment was put into use despite existing safety risks.
Inadequate Supervision
The investigation revealed that the contractor and stage engineering company had full control over the stage equipment but did not fulfill their responsibility to ensure its safety.
There was no evidence that the companies involved had taken any measures to guarantee that mechanical components and devices met safety and quality standards.
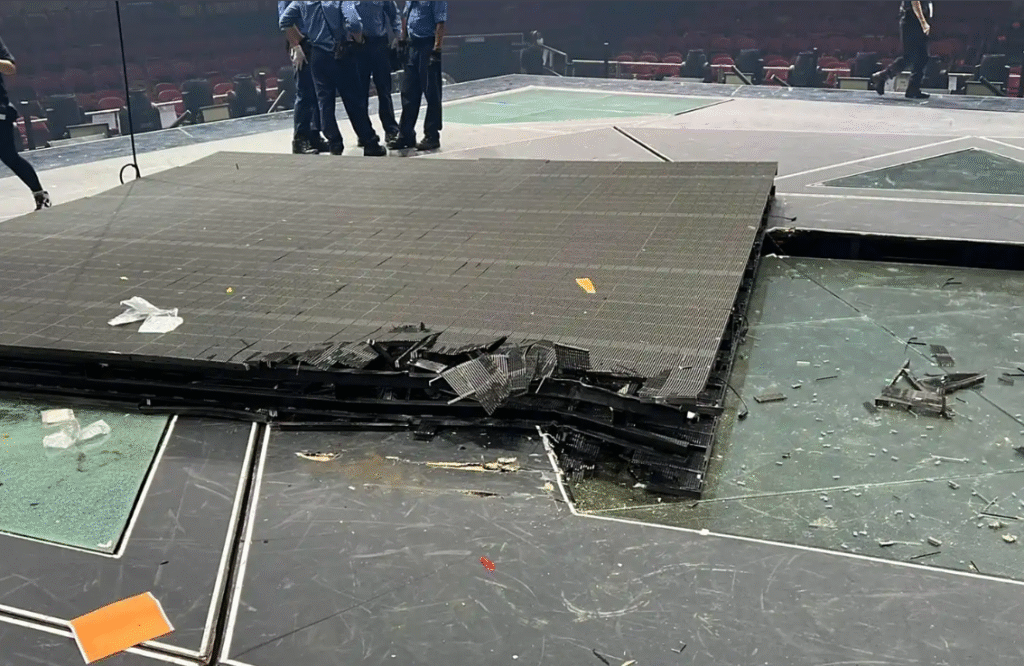

In-Depth Analysis: The Root Causes of the Incident
The investigation findings highlight that the Hung Hom Coliseum screen falling incident was not a mere accident but the result of multiple overlapping issues:
1. Lack of Full Lifecycle Equipment Management
The absence of comprehensive equipment management throughout the lifecycle of the stage equipment was a core issue in this incident. As a high-altitude suspended device, the LED screen required strict monitoring of its weight, load-bearing capacity, and service life. However, the responsible parties failed to implement a full lifecycle management system, resulting in overlooked equipment problems.
2. Weak Safety Awareness
The personnel involved failed to report or properly address the equipment issues they discovered, reflecting a lack of safety awareness among staff. This disregard for potential hazards directly led to the accident, underscoring the critical role of human factors in effective equipment management.
3. Inadequate Regulatory Mechanisms
The incident exposed significant gaps in Hong Kong’s regulatory framework for equipment management and safety supervision in large-scale performance events. The lack of unified standards and strict enforcement mechanisms allowed contractors and engineering companies to neglect their safety responsibilities.
4. The Trade-Off Between Cost and Efficiency
In an effort to save time and reduce costs, the companies involved opted for shortcuts, including falsifying data, while ignoring the importance of equipment management and safety. This short-sighted behavior ultimately led to an irreversible tragedy.
Solutions: How to Prevent Similar Incidents Through Equipment Management?
The Hung Hom Coliseum screen falling incident serves as a wake-up call for the performance industry, highlighting the urgent need for improvements in equipment management and safety supervision. Below are some practical solutions:
1. Implement Professional Equipment Management Software
The Hung Hom Coliseum screen falling incident revealed severe shortcomings in equipment management, which could have been avoided through the use of professional equipment management software. Currently, there are numerous advanced equipment management platforms available on the market. Among them, the SAMEX EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) platform is a comprehensive and efficient tool that provides systematic solutions for full lifecycle equipment management.

Full Lifecycle Management
In equipment management, full lifecycle management is the core aspect of ensuring safe operations. The platform provides comprehensive management for each asset, covering every stage from procurement to decommissioning:
- Procurement Stage: The platform records information such as the supplier, specifications, model, and procurement date of the equipment, ensuring that the equipment has a complete archive from the very beginning;
- Installation and Usage Stage: The system automatically generates installation records for the equipment and tracks its usage in real-time, helping businesses gain a comprehensive understanding of the equipment’s operational status;
- Maintenance and Servicing Stage: The platform automatically generates reminders based on the equipment’s lifecycle and maintenance plan, ensuring timely servicing to prevent aging or malfunctions caused by negligence;
- Decommissioning Stage: When equipment reaches the end of its service life, the platform promptly issues decommissioning alerts, preventing equipment from being used beyond its operational lifespan and eliminating potential safety hazards.
Through full lifecycle management, businesses can clearly monitor the status of each piece of equipment, ensuring that equipment operates in optimal condition at every stage. This significantly reduces the risk of accidents caused by mismanagement.
Task Standardization
Human error is often a major cause of safety incidents in equipment management. The platform offers robust task standardization features, enabling businesses to streamline and standardize equipment maintenance and inspection workflows.
The platform can automatically generate scheduled inspection tasks based on the type and usage frequency of the equipment and assign specific responsibilities for each task;
It also supports customizable inspection content, allowing businesses to set specific inspection items and standards according to their needs, ensuring that every inspection meets predetermined requirements;
Additionally, when equipment abnormalities occur, the system automatically generates temporary work orders and notifies relevant personnel to address the issue promptly, preventing problems from being ignored or delayed.
By using the SAMEX EAM platform, businesses can not only effectively reduce human errors but also significantly enhance the efficiency and transparency of equipment management. Furthermore, the standardization of inspection tasks facilitates enterprise oversight, ensuring that every task is executed properly.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
In the Hung Hom Coliseum incident, the LED screen involved had already exhibited problems before the accident occurred. However, due to the lack of real-time monitoring and alert mechanisms, the issues were not reported or addressed in time, ultimately leading to the tragedy. The platform’s real-time monitoring and alert features are key to solving this issue.
Using IoT (Internet of Things) technology, the platform connects to the equipment and collects real-time operational data, including critical indicators such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, helping businesses fully oversee the equipment’s operational status;
When the equipment’s operational data exceeds safe thresholds, the system automatically issues alerts and notifies relevant personnel via SMS, email, or app notifications, ensuring that issues are addressed promptly;
Additionally, the platform provides maintenance reminders based on the equipment’s servicing schedule, preventing failures caused by delayed maintenance.
With the real-time monitoring and alert features of the SAMEX EAM platform, businesses can address equipment issues at an early stage, significantly reducing the likelihood of equipment failures and safety incidents.
2. Strengthen Personnel Training and Safety Awareness
The professional competence and safety awareness of stage construction and equipment operation personnel are key elements in ensuring the safety of performances. Therefore, enterprises should place great emphasis on the training and management of relevant personnel. Regular professional skills training should be organized to ensure that all personnel are proficient in the technical essentials of stage construction, equipment installation, and operation. At the same time, they should understand the basic principles of equipment operation and the methods for handling common malfunctions, effectively reducing safety hazards caused by improper operations.
Secondly, safety awareness education should be strengthened. Through case studies, safety knowledge seminars, and other methods, employees should develop a deep understanding of the importance of safe operations and the severe consequences that may arise from violations, further reinforcing their sense of responsibility.
In addition, enterprises need to establish comprehensive accident emergency response plans and regularly organize emergency drills involving all employees. These drills should simulate the handling of emergencies such as fires, equipment failures, and stage collapses to ensure that every employee is familiar with the emergency procedures. This will enhance their ability to respond to emergencies and improve teamwork efficiency in critical situations.

3. Improve Regulatory Mechanisms
The safety supervision of stage equipment is a critical aspect of ensuring the safety of large-scale performances. Governments should establish unified safety standards for stage equipment, specifying detailed requirements for equipment selection, installation, and inspection. Strict supervision should be implemented for the installation and inspection processes of equipment used in large-scale events. Contractors should be required to have qualified engineers conduct comprehensive inspections after installation and issue safety certifications before the equipment is put into use. Regulatory authorities should also conduct on-site inspections and impose severe penalties on organizations that fail to comply with regulations or address safety hazards, thereby reducing the likelihood of accidents at their source.
Lessons from the Hung Hom Incident: The Importance of Equipment Management and Safety Supervision
The Hung Hom Coliseum screen falling incident has left a profound social impact and widespread trauma, all stemming from severe lapses in equipment management and safety supervision. These damages could have been avoided through standardized practices. If professional software tools had been introduced for equipment management to ensure effective lifecycle management, if regulatory enforcement had been strengthened to eliminate shortcuts, and if safety awareness and a sense of responsibility had been instilled through training, such tragedies could have been entirely prevented.
This incident serves as a stark reminder: safety is paramount, and equipment management and safety supervision must be central concerns for every industry. It is hoped that this painful lesson will prompt society to place greater emphasis on equipment management, improve regulatory measures, and take proactive steps to prevent harm before it occurs—because once harm is done, it is already too late.








