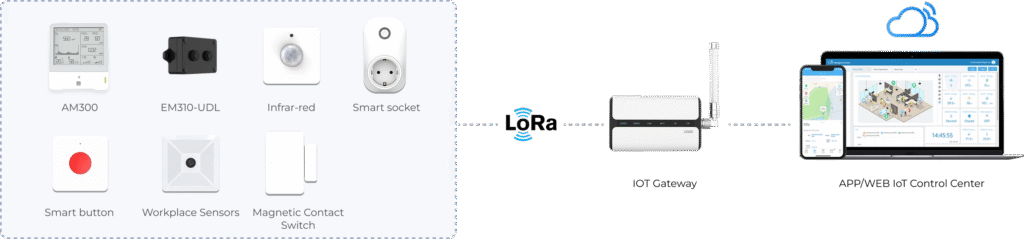
In the wave of enterprise digital transformation, asset management has shifted from “static registration” to “dynamic operation,” facing the pressure to transform from “passive control” to “proactive optimization.” Under traditional models, manual recording and isolated systems lead to mismatched records, sudden failures, and uncontrollable costs. Internet of Things (IoT) technology, combined with EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) software, is emerging as the key solution to break through these challenges. IoT utilizes sensors, smart plugs, control panels, smart switches, and other terminal devices to collect real-time asset data. This data is transmitted through LoRaWAN technology to IoT gateways, which then integrate with APP/WEB management platforms.
Meanwhile, the EAM system handles data consolidation, process control, and decision support. Together, IoT and EAM achieve four core objectives: “enhanced real-time monitoring,” “optimized maintenance and operational efficiency,” “reduced overall costs,” and “extended asset lifespan with improved ROI.” This combination upgrades asset management from “reactive response” to “proactive control,” building a full-chain, visualized, intelligent asset management system that provides robust support for maximizing enterprise asset value.
1. Pain Points in Traditional Asset Management and Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM’s Breakthrough Logic
Traditional enterprise asset management has long struggled with issues such as “data gaps, delayed responses, and high costs.” Asset status relies on manual inspections, making it impossible to capture operational anomalies in real time. Maintenance plans are based on experience, leading to either over-maintenance that wastes resources or untimely repairs that exacerbate failures. Asset locations and usage are difficult to trace accurately, resulting in high idle rates and a risk of loss. Data across different stages is scattered across isolated systems, failing to provide effective support for decision-making. These problems directly cause inefficiency in asset management, rising total costs, and difficulty improving asset ROI.
The advent of Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM has completely changed this situation. Its core logic lies in using smart terminals such as sensors, smart plugs, control panels, and smart switches to comprehensively collect data on asset location, operational parameters, and environmental conditions.
Leveraging LoRaWAN technology’s advantages of low power consumption, wide coverage, and strong interference resistance, data is stably transmitted to IoT gateways, aggregated, and synchronized with APP/WEB platforms, forming seamless data integration with EAM systems. This architecture enables asset data to be “visible, analyzable, and manageable” in real time, precisely addressing the four core demands of “enhanced real-time monitoring,” “optimized operational maintenance,” “cost reduction and efficiency improvement,” and “asset value enhancement,” propelling asset management into a new era of intelligence.
2. Core Value of Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM: Technological Paths to Achieve Four Key Goals
(1) Enhanced Real-Time Monitoring: Comprehensive Data Collection and Visualized Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) deploys diversified smart terminals combined with LoRaWAN transmission technology and IoT gateways to achieve 24/7, seamless monitoring of asset status. Sensors collect core operational data such as vibration, temperature, and energy consumption. Smart plugs monitor electrical load and power stability, while control panels and smart switches capture asset start-stop statuses and operational records. All data is transmitted via LoRaWAN technology with low latency to IoT gateways and synchronized with APP/WEB platforms.
Through APP/WEB platforms, enterprise managers can view real-time information on asset location distribution, operational parameters, and environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity, eliminating the need for on-site inspections. When data exceeds preset thresholds, the system pushes alarm notifications via the platform, enabling “real-time anomaly alerts.” For example, when a sensor detects that a production machine’s temperature exceeds the limit, the data is immediately uploaded via the IoT gateway, triggering an alarm on the APP/WEB platform. Managers can intervene promptly to prevent the fault from escalating. This comprehensive real-time monitoring capability effectively resolves the traditional asset management pain points of “invisibility and uncertainty.”
(2) Optimized Maintenance and Operational Efficiency: Data-Driven Precision Management
Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM upgrades asset maintenance from “reactive repairs” and “scheduled maintenance” to “predictive maintenance,” significantly improving operational efficiency. Smart terminals continuously collect asset operational data, which is transmitted via IoT gateways to the platform. Algorithms analyze asset health status and accurately predict potential failures. The system automatically generates maintenance work orders on the APP/WEB platform, specifying repair content, schedules, and responsible personnel, while linking to control panels for remote start-stop control, reducing on-site operational costs.
LoRaWAN technology’s wide coverage makes cross-regional, large-scale asset maintenance more efficient. For instance, in an industrial park with thousands of production machines, the architecture of sensors + LoRaWAN + IoT gateways allows managers to monitor all equipment status centrally via the WEB platform. The system prioritizes maintenance tasks based on operational data, avoiding blind inspections. Statistics show that using this solution improves maintenance response speed by 50%, reduces maintenance hours by 30%, and significantly optimizes operational scheduling efficiency, truly achieving “data-driven management instead of manual effort.”
(3) Reduced Overall Costs: Full-Chain Lean Management
Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM reduces overall asset management costs by minimizing resource waste, optimizing labor allocation, and lowering failure-related losses. In energy consumption management, smart plugs monitor real-time asset power usage, generating energy consumption reports on the APP/WEB platform. Managers can remotely shut down idle equipment via control panels or smart switches to reduce unnecessary energy consumption. In terms of labor costs, real-time monitoring and automated alerts replace traditional manual inspections, significantly reducing personnel requirements.
The APP/WEB platform’s remote management functionality eliminates the need for additional on-site staff for cross-regional asset management. In failure-related losses, predictive maintenance prevents sudden breakdowns that lead to production downtime, reducing repair costs and production losses.
For example, a manufacturing company applied this solution to monitor equipment energy consumption through sensors. Data was transmitted via IoT gateways to the WEB platform, revealing 30% of devices had standby energy waste. By optimizing operations and remote control through smart switches, the company reduced annual electricity costs by 25%, cut manual inspection costs by 40%, and decreased downtime losses by 60%, significantly lowering overall asset management costs.
(4) Extended Asset Lifespan and Increased ROI: Full Lifecycle Value Protection
Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM enables precise control across the entire asset lifecycle, effectively extending asset lifespan and improving ROI. During the usage phase, sensors and smart terminals monitor operational status to prevent damage from overload. During maintenance, the system develops precise maintenance plans based on equipment data, replacing aging components in time to avoid unnecessary dismantling damage. During idle phases, the APP/WEB platform displays real-time asset status, facilitating quick redeployment and reducing idle losses.
For instance, a logistics company equipped its vehicles with sensors and smart control panels. Using LoRaWAN technology and IoT gateways, it monitored real-time data on driving speed, engine temperature, and fuel consumption. The APP/WEB platform generated driving behavior analyses and maintenance recommendations, helping drivers optimize operations and maintain vehicles promptly. After implementation, vehicle failure rates dropped by 45%, lifespan extended by 3 years, and ROI increased by 28%. This full lifecycle value protection ensures that every asset investment delivers maximum returns.
3. Technical Architecture Advantages of Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM: Stable and Efficient Operations Enabled by LoRaWAN
The core advantages of IoT + EAM lie in its “smart terminals + LoRaWAN + IoT gateway + APP/WEB” full-chain technology architecture. Sensors, smart plugs, and other terminal devices are compact and versatile, adaptable to various asset types, whether production equipment, IT assets, or transport vehicles, enabling precise data collection. LoRaWAN technology’s features of low power consumption, wide coverage, and strong interference resistance make it ideal for industrial, campus, and other large-scale asset deployments, while its low transmission costs reduce long-term operational expenses.
IoT gateways serve as data hubs, ensuring efficient interconnection between terminal devices and platforms, while APP/WEB management platforms provide visualized interfaces accessible via computers and mobile devices, allowing managers to monitor asset dynamics anytime, anywhere.
This architecture ensures comprehensive data collection, reliable transmission, and lowers deployment barriers. Enterprises can quickly integrate IoT systems without extensive asset modifications, achieving seamless EAM integration and accelerating intelligent transformation.

4. Industry Applications: Practical Results of Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM
Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM has been applied across industries such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and campuses, demonstrating significant practical value. In manufacturing, an automotive parts supplier installed sensors and smart switches on production line equipment. Through LoRaWAN integration with IoT gateways, WEB platforms monitored equipment status in real time. The system generated maintenance plans based on data, pushing work orders to technicians via APP. Equipment failure rates decreased by 60%, maintenance costs reduced by 35%, and asset lifespan extended by 2 years.
In logistics, a company deployed smart terminals on vehicles and warehouse shelves, enabling real-time asset tracking and inventory management via IoT systems. Asset scheduling efficiency improved by 40%, and idle rates dropped from 30% to 8%. In office campuses, smart plugs and control panels integrated with IoT platforms achieved energy consumption monitoring and remote control of office equipment, saving over one million yuan annually in electricity costs.
These cases demonstrate that IoT + EAM, by successfully achieving four core goals, not only addresses traditional asset management pain points but also becomes a key driver for enterprises to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance competitiveness.
5. Future Trends: Deep Integration and Upgrades for Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM
As technology continues to evolve, IoT + EAM will advance toward greater intelligence and integration. In the future, AI algorithms will be deeply embedded in platforms, enabling precise failure predictions and automated scheduling. Digital twin technology will create virtual mirrors of assets, allowing full lifecycle simulation and optimization on APP/WEB platforms. IoT data will be fully integrated with ERP, CRM, and other systems, forming a unified management ecosystem that tightly links asset management with business development. Meanwhile, ongoing advancements in LoRaWAN technology will further enhance transmission speed and stability, supporting more complex asset management scenarios.
For enterprises, adopting Internet of Things (IoT) + EAM has become an inevitable choice in digital transformation. This technology solution enables real-time, precise asset management while effectively reducing costs and enhancing asset value, positioning enterprises for competitive advantage in the market.
Internet of Things (IoT) and EAM’s deep integration, supported by the “smart terminals + LoRaWAN + IoT gateway + APP/WEB” technology architecture, successfully achieves four core goals and reshapes enterprise asset management models. From comprehensive data collection for real-time monitoring to precise optimization of maintenance and operations, cost reduction, and sustained asset value enhancement, IoT not only addresses traditional asset management challenges but also imbues assets with “perceptibility, analyzability, and optimizability.”
As technology continues to mature, IoT will further empower enterprise asset management, driving industries toward higher efficiency, intelligence, and value, becoming the core driver of enterprise digital transformation.